H261 to AMRConvert H261 to AMR, H261 to AMR Converter |
 |
| Home | Getting Started | Download | Buy Now! | Screen Shots | FAQ | Support | Contact |
Total Audio MP3 Converter converts H261 files to AMR format. The software is an all in one audio converter that supports more than 90 audio and video files as input, and converts to popular formats such as MP3, WAV, AAC, M4A, OGG, WMA, and AMR. Total Audio MP3 Converter also supports batch conversion, and is full compatible with Vista and Windows 7.
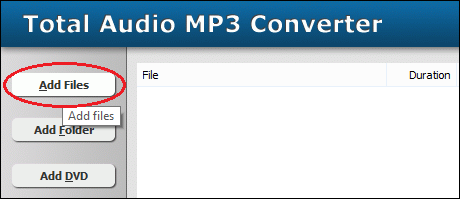 Click "Add Files" to choose H261 files and then add them to conversion list. 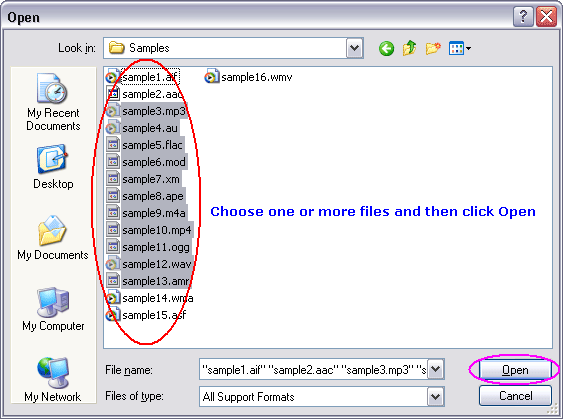 Choose one or more H261 files you want to convert and then click Open. 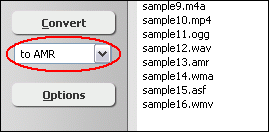  Click button "Convert" to convert H261 files to AMR format.  The software is converting H261 files to AMR format.  When conversion completes, you could right-click converted AMR file and choose "Play Destination" to play the outputted AMR file; or choose "Browse Destination Folder" to open Windows Explorer to browse the AMR file. What is H261? The H.261 standard actually only specifies how to decode the video. Encoder designers were left free to design their own encoding algorithms, as long as their output was constrained properly to allow it to be decoded by any decoder made according to the standard. Encoders are also left free to perform any pre-processing they want to their input video, and decoders are allowed to perform any post-processing they want to their decoded video prior to display. One effective post-processing technique that became a key element of the best H.261-based systems is called deblocking filtering. This reduces the appearance of block-shaped artifacts caused by the block-based motion compensation and spatial transform parts of the design. Indeed, blocking artifacts are probably a familiar phenomenon to almost everyone who has watched digital video. Deblocking filtering has since become an integral part of the most recent standard, H.264 (although even when using H.264, additional post-processing is still allowed and can enhance visual quality if performed well). What is AMR? Key Features:
Convert H261 to AMR Related Topics: H261 to AMR, M1V to AMR, VID to AMR, GSM to AMR, ALAW to AMR, VCD to AMR, EVO to AMR, XVID to AMR, MPGA to AMR, 3G2 to AMR, SHN to AMR, F4V to AMR, STR to AMR, SWF to AMR, DVR-MS to AMR, MPE to AMR, 3GP2 to AMR, PSX to AMR, THD to AMR, M2T to AMR, VOB to AMR, MTS to AMR, AMV to AMR, VOC to AMR, RPL to AMR, FLV to AMR, 3GP to AMR, ULAW to AMR, WMD to AMR, NSA to AMR, VMD to AMR, MTV to AMR, H264 to AMR, M1A to AMR, DV to AMR, OMA to AMR, DVD to AMR, M2TS to AMR, MP2 to AMR, DIVX to AMR
|
| Home | Getting Started | Download | Buy Now! | Screen Shots | FAQ | Support | Contact | Links |
| Copyright © 2008-2017 Hoo Technologies All rights reserved. Privacy Policy |